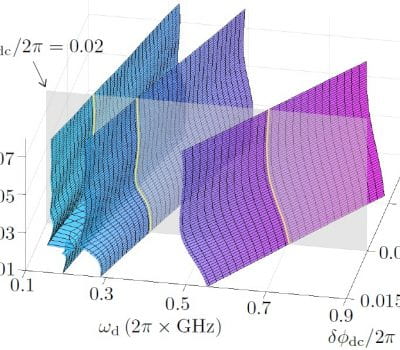
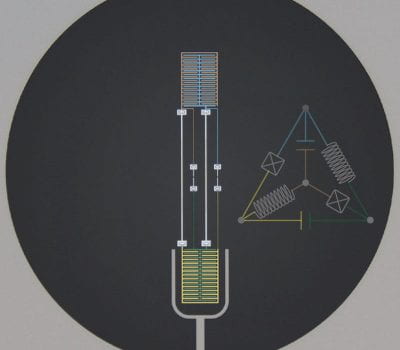
Protecting superconducting qubits from low-frequency noise is essential for advancing superconducting quantum computation. Based on the application of a periodic drive field, we develop a protocol for engineering dynamical sweet spots, which reduce the susceptibility of a qubit to low-frequency noise. Using the framework of Floquet theory, we prove rigorously that there are manifolds of […]
Author: Danny
New Phys. Rev. X Publication: Experimental Realization of a Protected Superconducting Circuit Derived from the 0 – π Qubit
In collaboration with the Houck group at Princeton, the Blais group at Sherbrooke, and David Schuster at UChicago, we provided theoretical support to the experimental realization of the 0–π circuit. Encoding a qubit in logical quantum states with wave functions characterized by disjoint support and robust energies can offer simultaneous protection against relaxation and pure dephasing. […]
New Nature publication: Protecting a bosonic qubit with autonomous quantum error correction
We provided theoretical support to our experimental colleagues at UMass Amherst on an experiment demonstrating autonomous quantum error correction. To build a universal quantum computer from fragile physical qubits, effective implementation of quantum error correction (QEC) is an essential requirement and a central challenge. Existing demonstrations of QEC are based on an active schedule of error-syndrome measurements and […]
New Phys. Rev. X Publication: Universal Fast-Flux Control of a Coherent, Low-Frequency Qubit
In collaboration with the Schuster Lab at UChicago, we provided theory support for an experiment studying the heavy-fluxonium circuit. The heavy-fluxonium circuit is a promising building block for superconducting quantum processors due to its long relaxation and dephasing time at the flux-frustration point. However, the suppressed charge matrix elements and low transition frequency make it […]
New Phys. Rev. Research Publication: Positive- and negative-frequency noise from an ensemble of two-level fluctuators
The analysis of charge noise based on the Bloch-Redfield treatment of an ensemble of dissipative two-level fluctuators generally results in a violation of the fluctuation-dissipation theorem. The standard Markov approximation (when applied to the two-level fluctuators coupled to a bath) can be identified as the main origin of this failure. The resulting decoherence rates only […]